Ergonomics and Eye Strain: Strategies for Mitigating Digital Fatigue
In an increasingly digital work environment, prolonged screen exposure has become a routine aspect of daily life. While technology enhances productivity and connectivity, it also introduces challenges to visual health—most notably, digital eye strain, also referred to as computer vision syndrome. This condition encompasses a range of symptoms including blurred vision, dry eyes, headaches, and musculoskeletal discomfort, often resulting from suboptimal ergonomic setups and extended screen time.
Understanding Digital Eye Strain
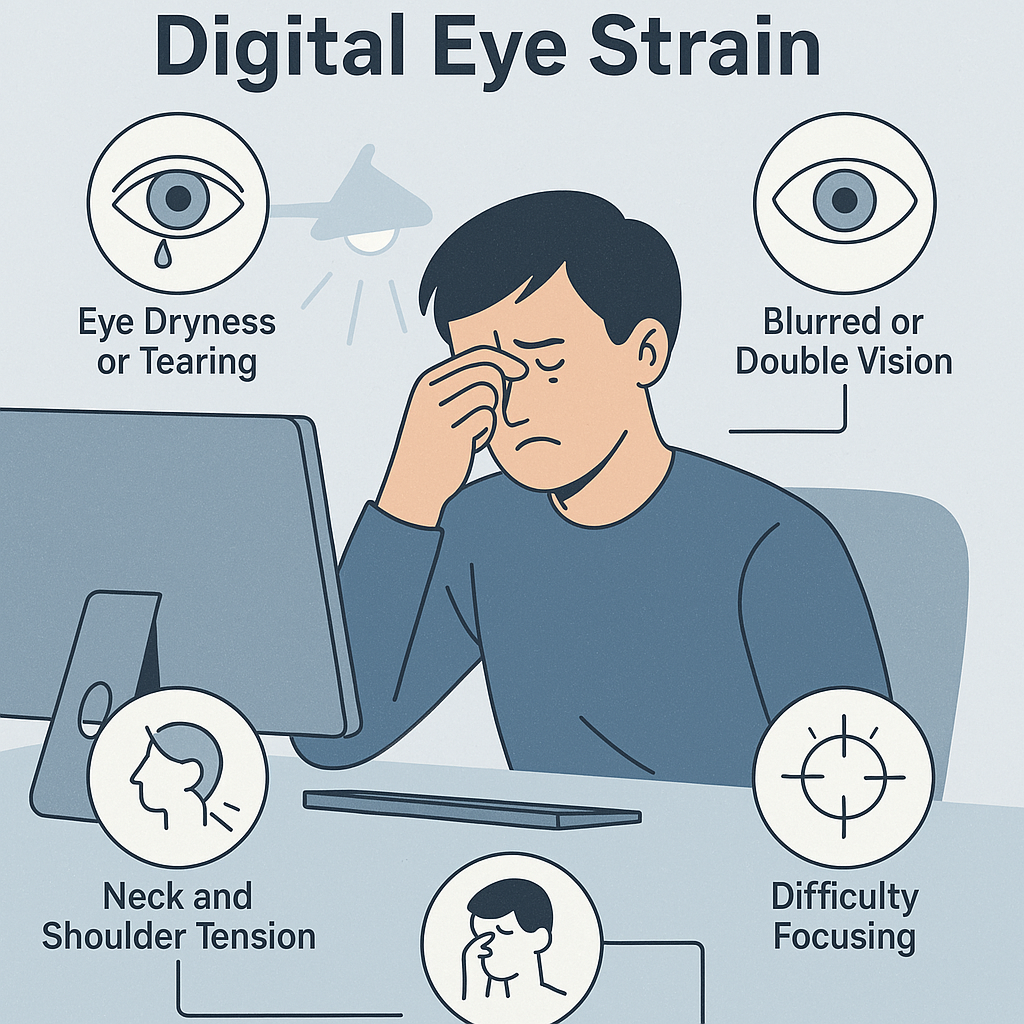
Digital eye strain arises when the visual demands of screen use exceed the capacity of the eye to comfortably focus and track. Common symptoms include:
Eye dryness or excessive tearing
Blurred or double vision
Eye strain or eye fatigue
Headaches
Neck and shoulder tension
Difficulty maintaining focus
These symptoms are frequently exacerbated by poor lighting, improper screen positioning, and insufficient visual breaks.
The Role of Ergonomics in Visual Comfort
Ergonomics is a critical factor in mitigating digital fatigue. A well-designed workstation not only supports musculoskeletal health but also promotes optimal visual ergonomics, reducing strain and enhancing overall comfort and productivity.
Strategies to Reduce Eye Strain:
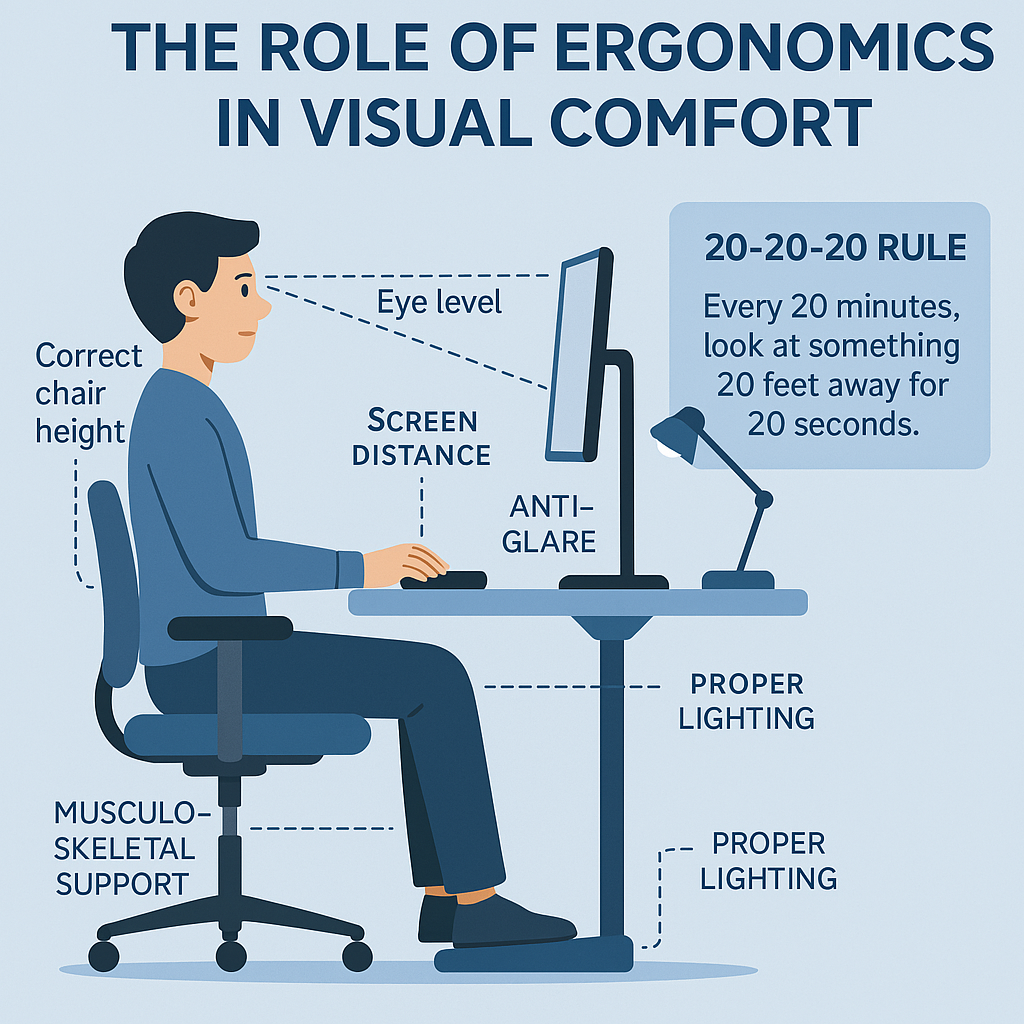
1. Implement the 20-20-20 Rule
Encourage regular visual breaks by following the 20-20-20 guideline: every 20 minutes, look at an object at least 20 feet away for 20 seconds. This practice helps relax the eye muscles and prevent fatigue.
2. Optimize Monitor Positioning
Maintain a viewing distance of approximately 20–30 inches from the screen. The distance varies because everyone’s vision requirement varies. Move the screens as close to your eyes where you do not feel like you want to lean forward to view the screen (keep ears over shoulders).
Position the top of the monitor at or slightly below eye level height.
3. Control Ambient Lighting and Glare
Use indirect lighting to minimize screen reflections. Position monitors perpendicular to windows to avoid direct sunlight. Consider installing anti-glare filters or using matte screen finishes.
4. Utilize Blue Light Reduction Tools
Enable blue light filtering features on devices or use specialized software to reduce exposure to high-energy visible (HEV) blue light, which may contribute to visual discomfort and sleep disruption. If possible, add a blue light filtering program such as F.Lux to your devise.
5. Adjust Display Settings
Increase font size and contrast to reduce the need for squinting and enhance readability. Customizing display settings can significantly improve visual comfort.
6. Encourage Regular Blinking
Screen use tends to reduce blink frequency, leading to dry eyes. Remind users to blink consciously or consider using lubricating eye drops to maintain moisture.
7. Consider Computer-Specific Eyewear
Prescription or non-prescription computer glasses can help reduce glare and enhance contrast or something like computer progressive lenses. Consult an optometrist for personalized recommendations.
Integrating Movement and Breaks
In addition to visual strategies, incorporating regular movement and posture changes can alleviate associated neck and shoulder tension. Encourage brief standing or stretching breaks every hour to support overall well-being.
Digital eye strain is a prevalent concern in modern workspaces, but it is manageable through thoughtful ergonomic design and proactive visual habits. By implementing these strategies, individuals can safeguard their visual health, enhance comfort, and maintain productivity in screen-intensive environments.